Physics or Fantasy
An Investigation of Modern Physics by Brian Williams-
The Invisible Crane Fly
Posted on April 11th, 2010 No commentsMany years ago I was breaking through an eighteen inch thick brick wall from outside. In a pause in my labours I became aware of a light buzzing noise close at hand. Concentrating on the noise I became convinced that it came from a small area in front of me, but I was unable to see any cause.
However, after a few more minutes the noise stopped and a crane fly appeared in the area I was watching. Watching the crane fly I hit the wall with my hammer and the crane fly immediately ‘disappeared’ again. Close scrutiny of the area allowed me to identify the lower few millimetres of the crane fly’s legs, but the rest of it was invisible. I carried out this procedure a few more times before blowing it away from the area that I was working in.
The question is, ”Is this a commonly known phenomena, or was it just a very clever crane fly that I was watching.”
Occasionally I have looked ‘crane flies’ up in various books, and recently on the internet, but have yet to find any mention of this ability.
Possibly this explains why when your wife gets you out of bed to kill an annoying crane fly and you miss the first attempt because you are still dopey, the crane fly ‘disappears’ even though you can still hear it, but you didn’t see it fly off as you would with a fly or wasp.
You can now ask “What has this got to do with physics?
Well, biology is part of physics (or should be), and crane flies are part of biology, and here we have an insect that can adopt a ‘cloak of invisibility’ (Magic) which it creates by means of classical mechanics, and all of modern physics can be explained by classical mechanics. Unfortunately, the physicists never seem to get beyond the ‘Magic’ stage of research. They have an inbred revulsion of mechanics which prevents them from progressing further. See Introduction
Note: My particular crane fly set up an oscillation in it’s body by rapidly moving it’s wings in a non-flying sequence. This oscillation is faster than the eye/brain can handle, therefore the crane fly ‘disappears’. This is indicative that the oscillation is just as effective with all of it’s natural predators, and thus that all it’s predators have the same optical frequency limitations that humans have.
It’s common British name “Daddy long Legs” indicates its most recognizable feature, which must be the main reason it can carry out it’s disappearing act, which would not be possible in a short legged insect. What we will never know is whether the oscillation initially had a different purpose (which may still be required) and the long legs evolved to provide the ability to ‘disappear’.
-
Complimentary Colours
Posted on April 1st, 2010 No commentsTry these simple experiments.
1. Stare at a Yellow coloured shape for about 30 seconds and then look at a white sheet. Make a note of what you see. Answer 1A
Carry out the same experiment again, but this time make a note of the background colour surrounding the shape. Answer 1B
Carry out the second experiment again but whilst still noting the background colour, note the colour of the shape. Answer 1C
2. Carry out the same experiments again but using a Red shape. Answers 2A, 2B, 2C
- Carry out the same experiments again but using a Dark Blue shape. Answers 3A, 3B, 3C.
Also carry out the same experiments, but instead of looking at a white sheet, just close your eyes.
It is essential that you carry out these experiments yourself without any input from me, otherwise I would be rightly accused of leading you.
The apparently strange results are due to the mechanics involved in the structure of the eye.
It could be advantageous to everyone (including me) if your results were published on this website so that the results would be available to all, and I could proceed to the next stage with a some independent experimental results.
Sadly, I have not received a single reply on this posting in 12 months.
-
Brownian Motion
Posted on March 31st, 2010 No commentsAnother part of the physicists file of silly hypotheses. Taught with much enthusiasm in schools, colleges and universities around the world, (mainly due to Einstein’s interpretation of its meaning), it consists of a small capsule full of liquid with a small quantity of pollen grains mixed in it. Observation of the mixture shows the pollen grains constantly on the move. Einstein claimed that this proved that molecules were in a constant state of movement on their own accord, and this molecular movement caused the pollen grains to move.
What was ignored, was that to see the pollen grains a high intensity beam of light was projected into the capsule. In my own Brownian Motion unit (Above), I estimate that between 350 and 500 watts of energy per litre of liquid are injected into the capsule, sufficient to boil away the liquid in a very short time. It is this energy injection that causes the movement of the pollen grains, not an inherent vibration of the molecules.
Einstein carried this strange hypothesis into his hypotheses regarding the gas laws, which further retarded the advancement of physics.
Short abstract from Physics or Fantasy – Section 2- Colour and the Quantum Theory – Brownian Motion.
Author – Brian Williams
-
Printer Colours
Posted on March 16th, 2010 No commentsThe printer colour cartridges Yellow, Magenta, and Cyan, are actually pale Yellow, pale Red ( Although some do have a small percentage of Blue) and pale Blue. They depend on the White of the paper and Black to create the various colour approximations.
In the lighter Yellow range control is by reducing the ratio of Yellow spots to allow more White to show through. In the darker Yellow range control is by adding varying ratios of Red or Black spots. If only Black spots are added it gives an impression of a darker Yellow, but if Red is added it gives an Orange/Yellow Ochre impression which people still consider to be Yellow. An artist will tell them differently.
In the lighter Red range control is by reducing the ratio of Red spots to allow more White to show through. In the darker Red range control is by adding varying ratios of Blue or Black spots.
In the lighter Blue range control is by reducing the ratio of Blue spots to allow more White to show through. In the darker Blue range control is by adding varying ratios of Red or Black spots. Black only gives a darker Blue.
Red only gives such Blues as Royal Blue etc. which have a higher energy than ‘true’ Blue.
Many papers have a distinct Yellow tint, and the White energy of ambient light, both affect our viewing of the finished print.
-
Projected Light
Posted on November 22nd, 2009 No commentsFig.1 shows the overlapping light beams as shown in most books on physics to try to convince the public that white light is composed of all the other colours.
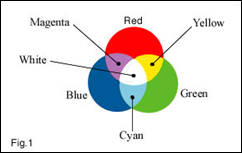
Unfortunately the illustration does not show the actuality, because there are no neat uniform areas of colours as shown. The light projectors do not project an even circle of colour as shown because the high intensity white beam always shows through the filters.
Consider the following extract: ‘It is an advantage if the projectors are controlled by rheostats, so that the relative intensities can be controlled in order to produce a good white’. From PHYSICS – An Examination Course. By E. L. Hansen. Hulton Educational Publications Ltd. In other words, if the physicists cannot obtain the results that they want, they are allowed to cheat. To be fair they don’t understand that it is cheating.
If you look at a Blue filter lying on a white sheet you see an even blue shade across the whole filter. If you shine a light through any filter you get results similar to those shown below.

It is obvious that a considerable amount of white light is coming through the filters. If we re-label the above drawing to allow for this white light we arrive at the following drawing.
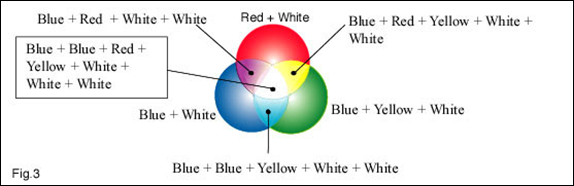
In the above drawing we are looking at the combined colour energy levels in particular areas. We are also getting dangerously close (If you are a physicist) to the artists colour mixing principles.
In the ‘Yellow’ area the combination of colours would give a yellow ochre. In the ‘White’ area the combination would give a very light grey. The white intensity from the lamps is very much higher than the white intensity from a ‘White’ screen, and therefore a relatively small amount of white light has a far greater impact than you would expect. Referring back to the chapter on the energy value of coloured light, the white light from the lamps has a probable intensity of at least 10 times greater the yellow light from the filters.
See ‘The Origin of Colour’, Taper Slit experiment, Taper Silhouette Experiment.
Technorati Tags: Projected Light,Colour,Colour – New Experiments,First published November 22nd 2009 -
Colour – Williams’ Taper Silhouette Experiment
Posted on November 22nd, 2009 No comments.
For our second experiment we use a tapered silhouette as shown.

If you view this silhouette through a prism you will see a spectrum as shown below.

In the above view the Blue and Red bands are forced into occupying the same space, therefore the combined energy plus some turbulence gives us Magenta. Where you would expect Green i.e. where the Blue and Yellow bands cross, you have the extra energy of the Red light in the Magenta which is being squeezed into the same area. This forces the total energy back into White. This I refer to as a ‘compression spectrum’.
It should be remembered that in the slit experiment the light can expand into the dark area. In the silhouette the colour bands are under pressure from the surrounding White light. Regarding the hypothesis that Yellow light is a combination of Red light and Green light, there is no evidence of any Green light. If there was a Green band between the Yellow band and the surrounding White I might have been interested in the hypothesis.
Note: Light acts in exactly the same way as any fluid, and follows the laws of fluid dynamics.
Abstract from Physics or Fantasy – Section 2 – Colour and the Quantum Theory
See also Williams’ Taper Slit experiment
-
Colour – Williams’ Taper Slit Experiment
Posted on November 8th, 2009 No commentsTo demonstrate that Green and Magenta are not ‘Primary’ colours, the following simple experiments are presented. For the 1st experiment, we have a tapered slit in place of the normal parallel slit.

If you view this slit through a prism you will see a spectrum as shown below: –

- As the Yellow and Cyan (Bright Blue) bands overlap the result is Bright Green.
- As the Red and Blue bands overlap the result is Purple.
- As the Yellow and Blue bands overlap the result is a Mid Green.
- As the Cyan and Red bands overlap the result is Mauve (Light Purple).
These are exactly the same as the artist’s mixing rules.
The physicist’s distorted ‘Standard’ spectrum forces them to argue that a completely different set of physics laws must apply to light.
Notes
- At the thin end of the slit the amount of light passing through is drastically reduced and makes it difficult to accurately determine the colours.
- The Cyan band is caused by the interference effect between White and ‘true’ Blue.
You will notice that there is no Magenta involved. Magenta requires a certain amount of compression to create the additional energy and should not be confused with the Mauves and Purples.
The Slit and Taper Slit spectra are what I call ‘Expansion Spectra’.
Short extract from Physics or Fantasy – Section 2 – Colour and the Quantum Theory.
-
Colour and the Prism
Posted on October 26th, 2009 No commentsWe are taught at school that a prism splits White light into its component colours. This is not true. Pass White light through a prism and you get White light. You cannot see a spectrum through a prism unless there is an edge visible. It is the edge that creates the colours, by reducing the energy of the light passing the edge, in the same way that water passing through an orifice has a reduced flow-rate adjacent to the edge of the orifice.
“Grimaldi has inform’d us, that if a beam of the Sun’s light is be let into a dark room through a very small hole, the…, and that these shadows have three parallel Fringes, Bands or Ranks of colour’d Light adjacent to them.”
From Sir Isaac Newton’s ‘The Third Book of Opticks’, fourth edition, first paragraph, originally published 1730, Dover Publications, Inc, New York. Standard Book Number: 486-60205-2
It is clear therefore that the creation of colours by an edge has been known to science for nearly 300 years. However I have never seen any mention of this in any modern book on physics.
This discovery by Grimaldi – Italian physicist – (1618-1663) was quite important, but its main significance was missed by the physics establishment, (Possibly not true of Newton, because he was quite devious in many ways, and his inclusion of the above paragraph as the introduction to Book Three would indicate that it had particular importance to him.)
It is also obvious from the above that the edge creates THREE colour bands, not 6 or 10 or 20 or 50. These bands are the Dark Blue, Red and Yellow referred to in this web site. from which all other colours are derived. Although you can understand it being missed 300 years ago, there is no excuse in modern times for this evidence being ignored. The problem was (and still is), that it had already been accepted by the physics establishment that White light was a combination of all the other colours.These coloured edges are commonly visible when looking through windows at a bright sky. The window is a wide slit. The shadows on both sides of a beam of light coming through a slit have coloured edges. We should really say that the White light passing through the slit has differently coloured edges.
A prism does not split White light into the different colours. but makes the colours created by the edges of a slit more readily discernible. If the slit becomes too narrow the coloured edges meet and give the distorted and blurred spectrum that physicists claim as a ‘true spectrum’.
See also Taper Slit Experiment, Taper Silhouette ExperimentFirst Published October 26th 2009 -
Colour Filters- The Mechanics.
Posted on October 26th, 2009 No commentsPhysicists have never grasped the mechanics of colour or colour filters.
Most books on physics claim that Yellow is not a primary colour and that it is a combination of Green and Red light. This is based on the fact that both Yellow and Blue light will pass through a Green Filter. They say that Blue does not pass through a Red filter, which is untrue. They also claim that Red will not pass through a Blue filter, which is also untrue. In fact the filters reduce the energy of any light passing through them. White light passing through a Yellow filter will have its energy reduced into the Yellow range. The Red filter reduces the light into the Red range, and the Blue filter further reduces the light into the Blue range. The Yellow light exiting the Yellow filter carries some White light, the Red light exiting the Red filter carries some Yellow light and the Blue light exiting the Blue filter carries some Red light. The lower the energy of the light the easier it passes through a filter. White light passing through a Blue filter always gives you Blue plus White.
In the sketch below the Blue light passes through the yellow filter easily but the residual White from the Blue filter picks up some Yellow light, therefore creating a Dark Green. The higher energy Yellow is mostly reduced to Red while passing through the Red filter, leaving the lower energy Blue to pass through without difficulty.
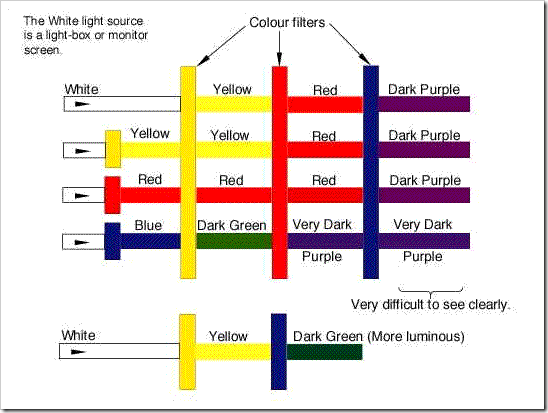
Colour filters are not really filters they are optical resistances. They reduce the energy of light passing through them, they do not filter anything out of the light. A light beam loses energy by reflection and heat. A beam of White light striking the surface of a filter reflects a considerable amount of White light. The darker the filter, the greater the energy lost to reflection. A Dark Blue filter reflects almost White light, a Red filter reflects a bright Rose Pink, and a Yellow filter reflects a distinct Yellow. Energy is lost in the heating up of the filter itself, again the darker the colour the greater the heat loss.
Note: None of the ‘standard’ colours of pigments, or the RGB, CYMK, etc of monitors can produce the actual ‘true’ primary colours. The colours in the above drawing are only approximate. The closest are Red, Navy, and a slightly deeper version of the Yellow. With the addition of White and Black all other colours can be produced from these. See ‘Origin of Colour’
The colour of light passing through a filter depends on various conditions. It depends on the intensity of the light source and the colour of the light source. The simple experiment below demonstrates the type of logic error common in physics research. The left hand sketch shows white light reflected from a White card and then passing through a Red filter. Most people consider that if they lay a Red filter on a white board then the White light from the board shines through the filter in the same way as the left hand sketch. This is not true, because the light passing through the filter from the board is Red, not White, as indicated in the right hand sketch.
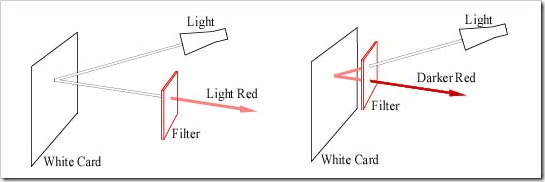
Why can a lower energy colour such as Blue pass easily through Red and Yellow filters, yet higher energy colours like Red and Yellow have difficulty passing through a Blue filter? The answer is simple mechanics.
The light passing through a filter may be compared with well-protected dodgem cars travelling along a wide highway that is scattered with large concrete blocks. The cars travelling at low speed will be able to negotiate these obstacles without mishap, and without much loss of speed. If the speed increases there will be collisions with the obstacles or other cars. The greater the speed, the greater the chance of collisions occurring. Comparing with light filters, the Blue filter would have many concrete blocks; Red would have less and Yellow even fewer.
It is obvious that the lower speed cars would have no difficulty passing through areas with fewer concrete blocks. This means that the cars (Particles) having the least energy have the least difficulty in passing through the obstacle course (Filter).
The interactions between cars (Particles) would be considerable, collisions causing some cars to accelerate and others to be slowed down, and some to be deflected off the side of the road (Heat emission). Some of the higher speed cars could pass through the area with little loss of speed, slight collisions with other cars deflecting them away from concrete blocks.
While on the subject of filters let us look at some others aspects of the physicists hypotheses on colour. Consider the arguments that White light is composed of all the other colours. This is on the basis that all other colours can be obtained from White light. This is a very weak hypothesis. If you have a 120 volt power supply you can obtain 100v, 24v, 12v, 6v, 3v or 1.5v from it. This does not mean that a 120 volt power supply is made up of all the lesser voltages.
As already shown you can obtain Red, Blue and Green light from Yellow light. This does not mean that Yellow light is made from Red, Blue and Green light.
The physicists statements that Blue light has the greatest energy is based on the illogical argument that “in a deep filter only Blue light passes through it and this proves that Blue light must have more energy.” Obviously they are forced to this conclusion by their conviction that White light is a combination of all the other colours. Using the same type of “logic” they could claim that as the water coming from the end of a 10km long x 25mm diameter. pipeline is only at a very low pressure, then this proves that only very low pressure water has the energy to travel this far!
Green Filters.
There are a lot of hits on the subject of Green filters. White light passing through a Green (mixed pigments of Yellow and Blue.) filter, results in a mixture of White, Yellow, Blue and normally a small amount of Red. (See Projected Light). The Red comes from a small amount of the Yellow light losing enough energy to fall into the Red range.
The colour seen through a filter depends on the make-up of the particular filter. If a green filter is a mixture of 10% Yellow and 90% Blue pigments, then approx. 10% of Yellow light will pass through. However, if the filter is 90% Yellow and 10% Blue then the light will probably contain a larger proportion of Red. The Yellow pigments will allow Yellow, Red and Blue light to pass through, the Blue pigments will only allow Blue light through, (With a touch of Red). This problem applies to all colour filters. A Royal Blue pigment is a mixture of Blue and Red pigments. Only by determining the basic ‘True Colours” can we create a scientific basis for colour, and form a common standard based on the actual physics of colour.
When considering colour filter set-ups it is essential to look at the mechanics of the system.
Consider where White light passes through a Red filter, reflects off a Green coloured board, and the board is viewed through the Red filter. The physicists argue that the Green is seen as Black through the Red filter. This is not so.
Green is a mixture ‘true’ Blue, (a very dark Blue), and ‘true’ Yellow, the actual shade depending on the relative proportions. The residual White light (See Projected Light) is reflected off the Green board as a mixture of ‘true’ Blue and ‘true’ Yellow light, and the Red light exiting the filter will be reflected off the Yellow pigment as Red and off the Blue pigment as Blue.. The Blue, on the second pass, will easily go through the Red filter but the Yellow light is mainly reduced into the Red range. We are therefore looking at a very dark Purple colour, which, under normal viewing conditions is easily mistaken for Black.
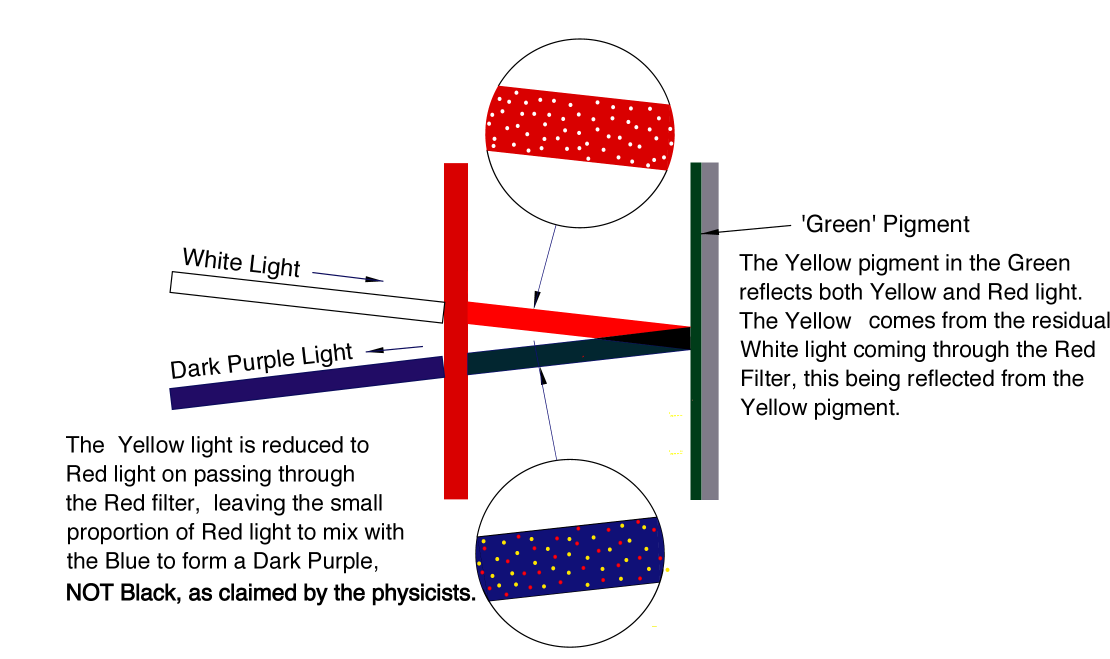
Reflected Green Light
If the Green is a light Green, this may because it has a greater proportion of Yellow pigment, or because it has a percentage of White pigment included. In this situation the Green board will appear to be a lighter purple.
A bit complicated, but mechanics is complicated, the main reason physicists can’t understand it.
Author, Brian Williams
GO TO “Master Page – Index” for related Colour posts that will help you to understand colour.
Technorati Tags: Colour Filters -
Newton’s Colour Wheel – The Reality
Posted on October 26th, 2009 No commentsModern physics considers that Newton’s rotating disc experiment proves that White light is composed of a combination of colours. The original experiment consisted of a rotating disc painted with various coloured sectors. As the speed increases the colours blur and become a greyish colour. The argument that this proves that White light is composed of the different colours is totally untrue. Most paints and dyes include white pigments to obtain the lighter shades. As the disc rotates the reflected light is a mixture of Blue, Red, Yellow and White light
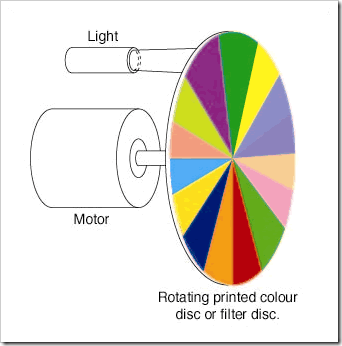
The predominant pigment seen is White and this is seen for most of each rotation of the wheel. If 10 of the 15 sectors contain White pigment then White light will be seen for 2/3rds of each revolution.
If there are Red pigments in 5 of the 15 sectors then Red light will be seen for 1/3rd of each revolution. Similarly for Blue and Yellow pigments.
Also of importance is the relative energy of the reflected light. The White light has considerably more energy than the other colours and will therefore have a greater affect than just its relative proportion. Yellow will have a greater affect than Red or Blue, etc..
If we use a filter disc and shine a White light through it, we have a similar situation. Most filters allow some white light through them. In general therefore we will see White light for 100% of each revolution of the wheel. The points in the previous paragraphs also then apply.
The actual shades and percentages of pigmentation will determine the shade of ‘Grey’ seen.
If we had 25% each of Blue, Red, Yellow and White pigments, then the reflective energy of the 25% White would probably be greater than the combined energies of the other colours.
Note that what if we look at a sheet of ‘White’ paper whilst inside a well lit room, it reflects only about 10% of the energy that it would if viewed outside on an overcast day. It still appears to be White in both locations.
The retinal cones are also confused by the constant colour changes above 16 changes per second. The relative constancy of the White during each revolution allows the cones to easily identify White.
Although normally used to ‘obtain’ varying shades of Gray, the colour wheel can be used to produce any colour by using only White, Yellow, Red, Dark Blue and Black sectors in varying proportions.
If the wheel only has Yellow and Blue pigment sectors or filters the colour seen is Green, therefore ‘proving’ that Green light is composed of Yellow and Blue light. If you only use Red and Green on the wheel you get Gray/Khaki, not Yellow as argued by the physicists. This is using the same principles/hypotheses as the physics establishment.
However, if you force (Yellow + Blue) = Green + Red into the same space the total energy (Speed) increases into the Yellow range or even sometimes into White. Basic Fluid mechanics.
Author.-Brian Williams
See An Introduction to Colour for further information.
See also Projected Light , Colour and the Prism andTechnorati Tags: Newton’s Colour Wheel


